MySQL - 索引的使用
MySQL - 索引的使用
- 索引的使用
- 验证索引提升查询效率
- 准备环境
- 避免索引失效
- 1).全值匹配 ,对索引中所有列都指定具体值。
- 2).最左前缀法则
- 3).范围查询,不能使用索引 。
- 4).不要在where中对索引列进行运算操作或函数操作,否则索引将失效。
- 5).当数据类型出现隐式转换时,比如 varchar 不加单引号可能转换为 int 类型时,会使索引无效,触发全表扫描
- 6).尽量使用覆盖索引,避免select
- 7).用or分割开的条件, 如果or前的条件中的列有索引,而后面的列中没有索引,那么涉及的索引都不会被用到。
- 8).以%开头的Like模糊查询,索引失效。
- 9).如果MySQL评估使用索引比全表更慢,则不使用索引。
- 10).is NULL,is NOT NULL 有时索引失效。
- 11).in走索引,not in 索引失效。
- 12).单列索引和复合索引。
- 13).使用OR
- 14).使用order by
- 15).使用<>,!=
- 查看索引使用情况
- 练习
# 索引的使用
索引是数据库优化最常用也是最重要的手段之一, 通过索引通常可以帮助用户解决大多数的MySQL的性能优化问题。
# 验证索引提升查询效率
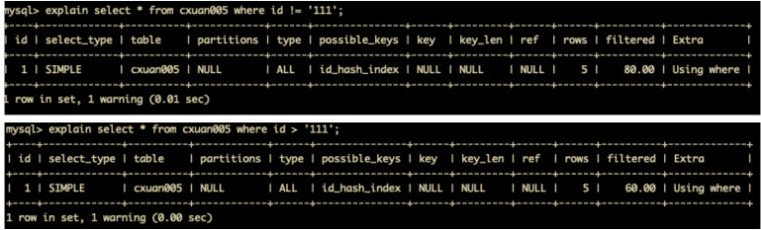
在我们准备的表结构 tb_item 中, 一共存储了 300 万记录;
1). 根据ID查询
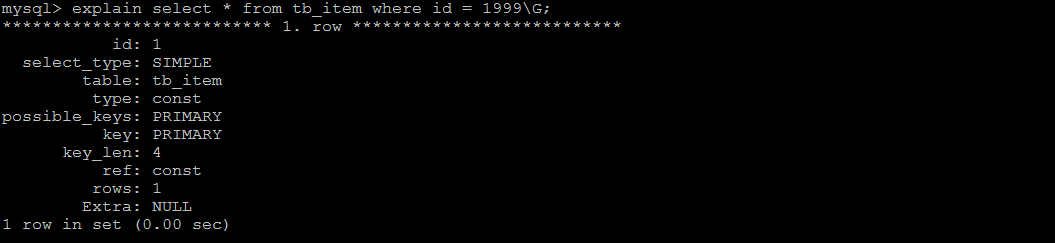
select * from tb_item where id = 1999\G;
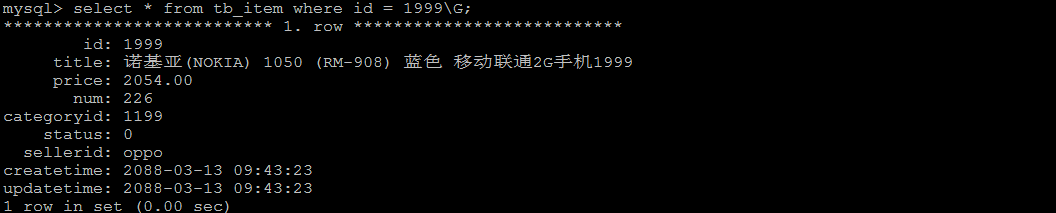
查询速度很快, 接近0s , 主要的原因是因为id为主键, 有索引;
2). 根据 title 进行精确查询
select * from tb_item where title = 'iphoneX 移动3G 32G941'\G;
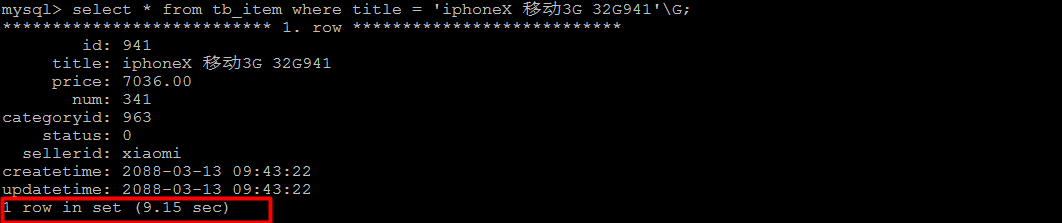
查看SQL语句的执行计划 :
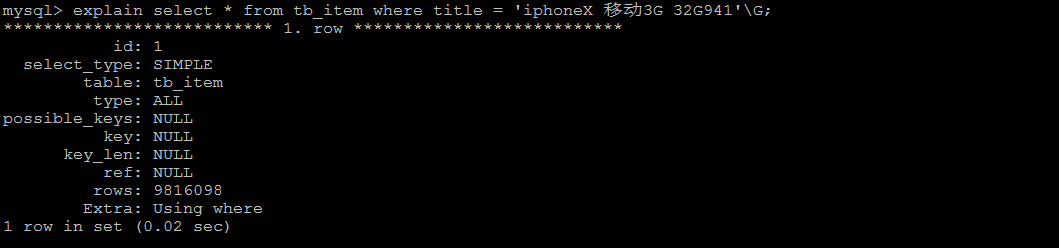
处理方案 , 针对title字段, 创建索引 :
create index idx_item_title on tb_item(title);

索引创建完成之后,再次进行查询 :
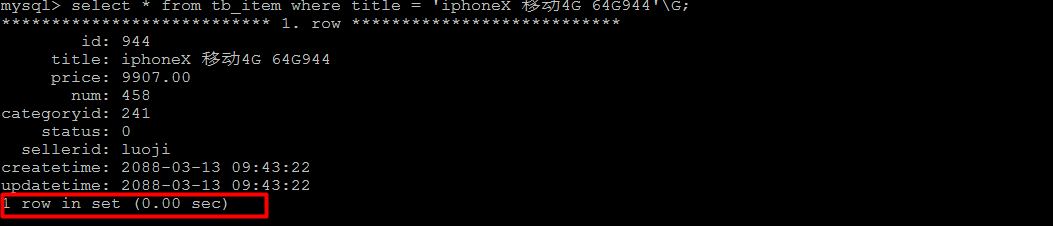
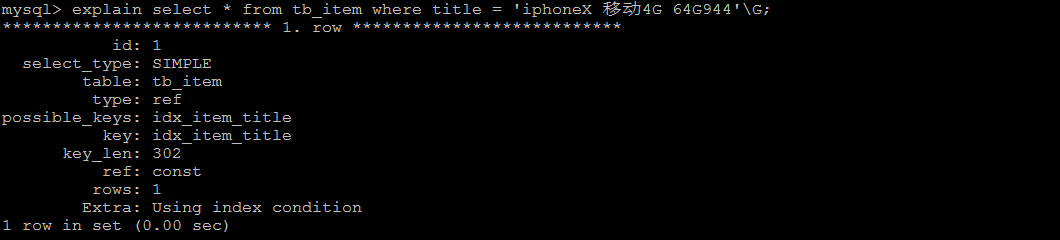
通过 explain , 查看执行计划,执行SQL时使用了刚才创建的索引
# 准备环境
create table `tb_seller` (
`sellerid` varchar (100),
`name` varchar (100),
`nickname` varchar (50),
`password` varchar (60),
`status` varchar (1),
`address` varchar (100),
`createtime` datetime,
primary key(`sellerid`)
)engine=innodb default charset=utf8mb4;
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('alibaba','阿里巴巴','阿里小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('baidu','百度科技有限公司','百度小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('huawei','华为科技有限公司','华为小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','0','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('itcast','传智播客教育科技有限公司','传智播客','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('itheima','黑马程序员','黑马程序员','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','0','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('luoji','罗技科技有限公司','罗技小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('oppo','OPPO科技有限公司','OPPO官方旗舰店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','0','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('ourpalm','掌趣科技股份有限公司','掌趣小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('qiandu','千度科技','千度小店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','2','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('sina','新浪科技有限公司','新浪官方旗舰店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('xiaomi','小米科技','小米官方旗舰店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','西安市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
insert into `tb_seller` (`sellerid`, `name`, `nickname`, `password`, `status`, `address`, `createtime`) values('yijia','宜家家居','宜家家居旗舰店','e10adc3949ba59abbe56e057f20f883e','1','北京市','2088-01-01 12:00:00');
create index idx_seller_name_sta_addr on tb_seller(name,status,address);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
# 避免索引失效
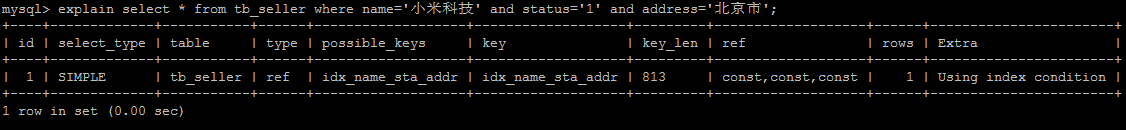
# 1).全值匹配 ,对索引中所有列都指定具体值。
该情况下,索引生效,执行效率高。
explain select * from tb_seller where name='小米科技' and status='1' and address='北京市'\G;
# 2).最左前缀法则
如果索引了多列(复合索引),要遵守最左前缀法则。指的是查询从索引的最左前列开始,并且不跳过索引中的列。
注意:如果使用了全值匹配,未遵循最左前缀原则,也能够完美走索引,因为全值匹配时,如果顺序与索引字段顺序不对,MySQL底层的SQL优化器会对此进行优化,从而达到能走索引的效果
匹配最左前缀法则,走索引:
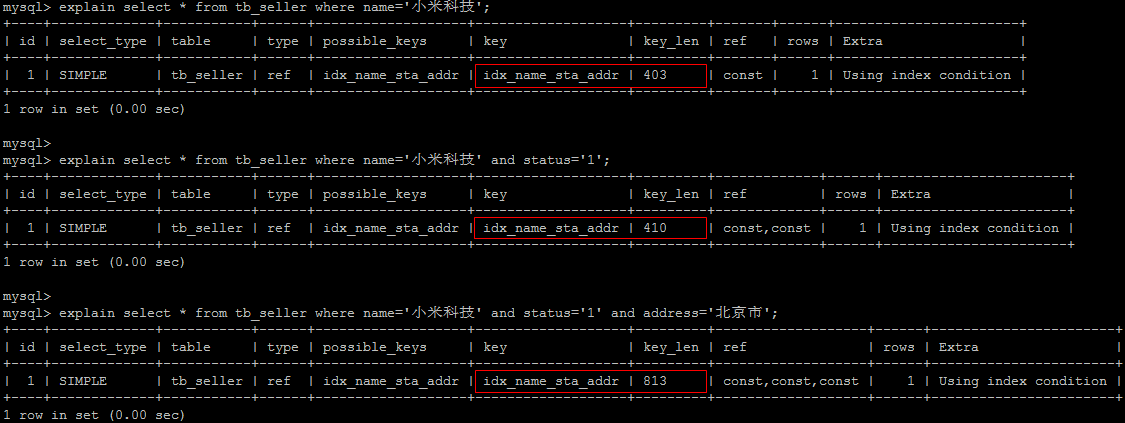
违反最左前缀法则 , 索引失效:这里是查询索引的第二个字段,导致失效。查第三个字段也会失效
如果符合最左法则,但是出现跳跃某一列,只有最左列索引生效:
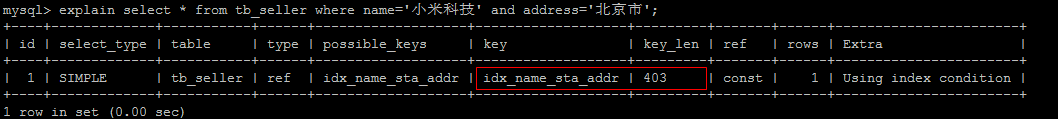
# 3).范围查询,不能使用索引 。
根据前面的两个字段name , status 查询是走索引的, 但是最后一个条件address 没有用到索引。
# 4).不要在where中对索引列进行运算操作或函数操作,否则索引将失效。
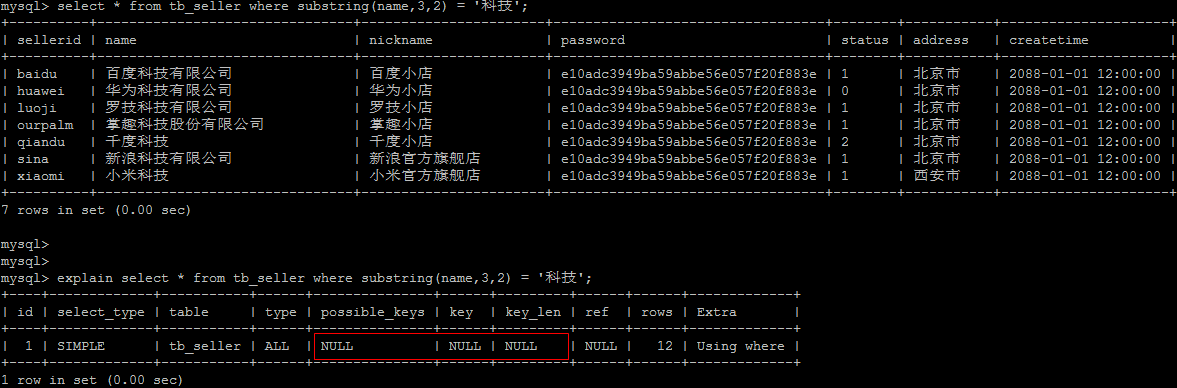
# 5).当数据类型出现隐式转换时,比如 varchar 不加单引号可能转换为 int 类型时,会使索引无效,触发全表扫描
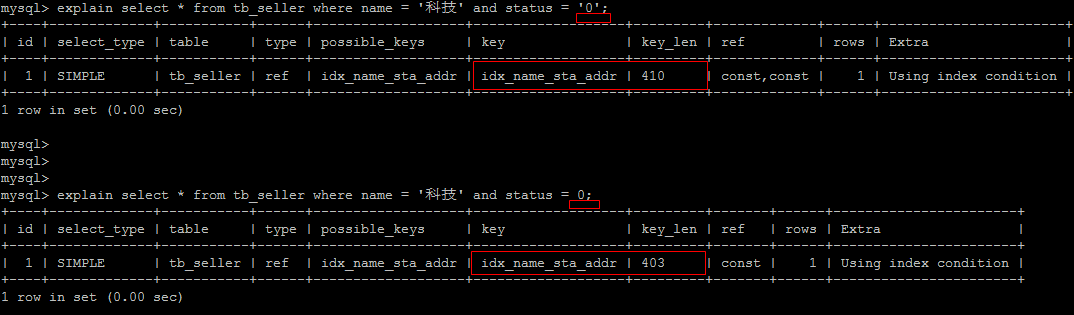
在查询时,没有对字符串加单引号,MySQL的查询优化器,会自动的进行类型转换,造成索引失效。
# 6).尽量使用覆盖索引,避免select
尽量使用覆盖索引(只访问索引的查询(索引列完全包含查询列)),减少select * 。
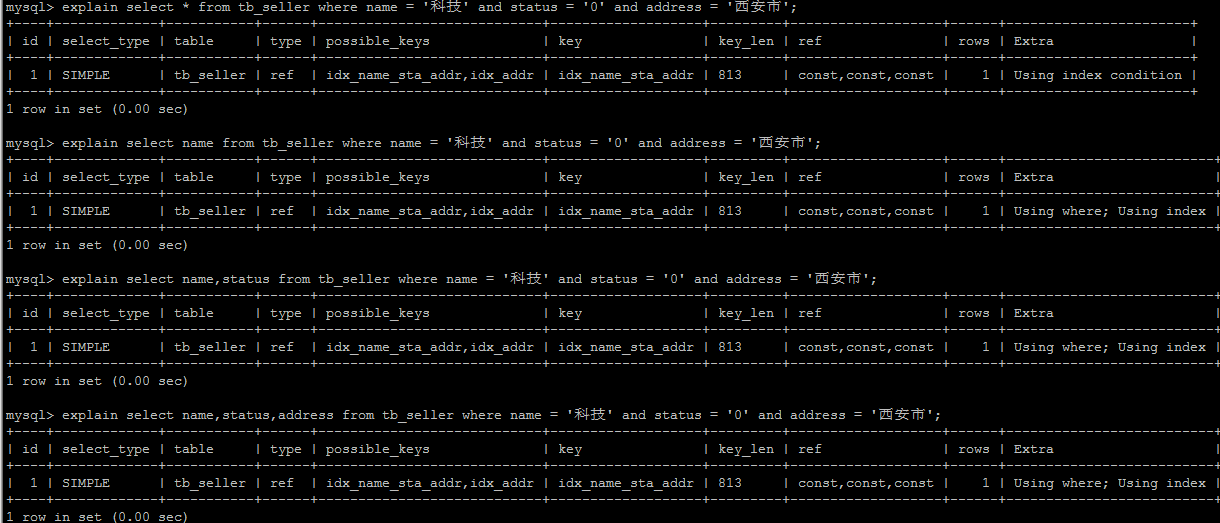
如果查询列,超出索引列,也会降低性能。
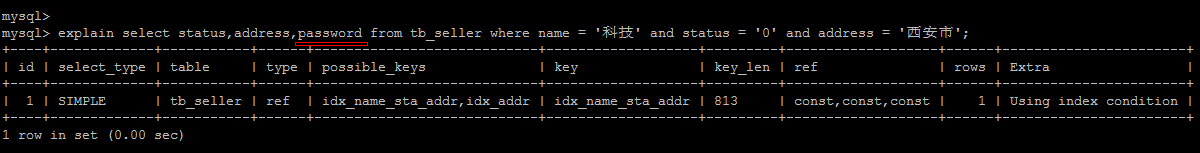
Extra:
using index
使用覆盖索引的时候就会出现
using where
在查找使用索引的情况下,需要回表去查询所需的数据
using index condition
查找使用了索引,但是需要回表查询数据
using index ; using where
查找使用了索引,但是需要的数据都在索引列中能找到,所以不需要回表查询数据
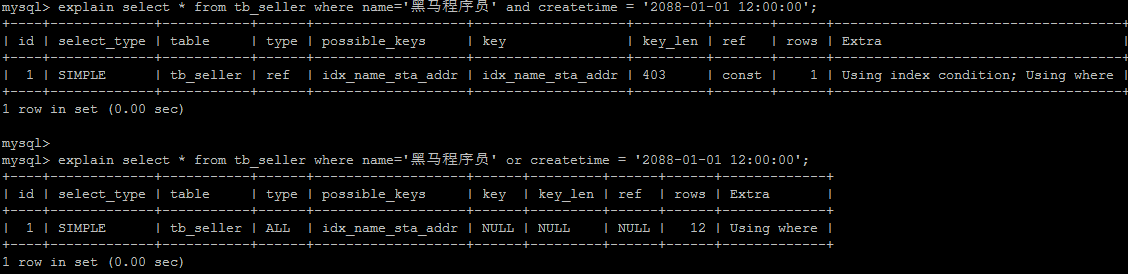
# 7).用or分割开的条件, 如果or前的条件中的列有索引,而后面的列中没有索引,那么涉及的索引都不会被用到。
示例,name字段是索引列 , 而createtime不是索引列,中间是or进行连接是不走索引的 :
explain select * from tb_seller where name='黑马程序员' or createtime = '2088-01-01 12:00:00'\G;
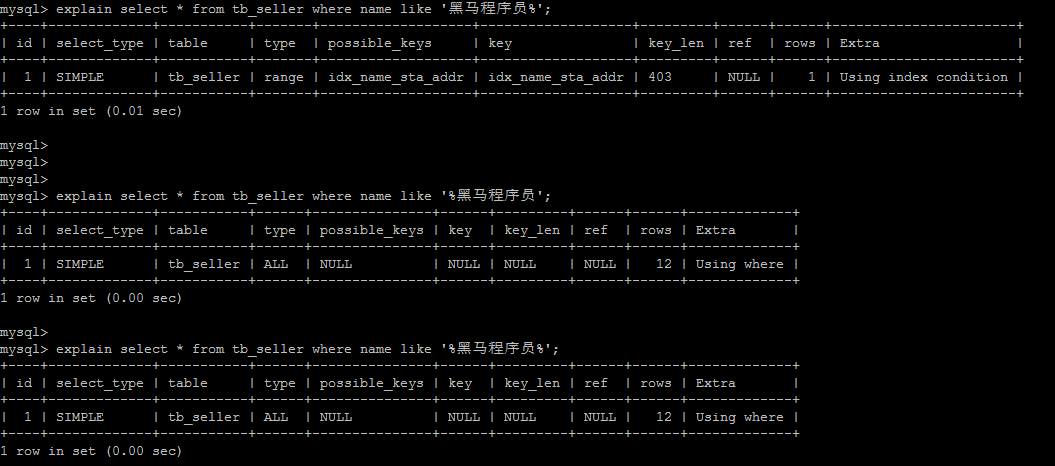
# 8).以%开头的Like模糊查询,索引失效。
如果仅仅是尾部模糊匹配,索引不会失效。如果是头部模糊匹配,索引失效。
explain select * from tb_seller where name like "%黑马程序员";
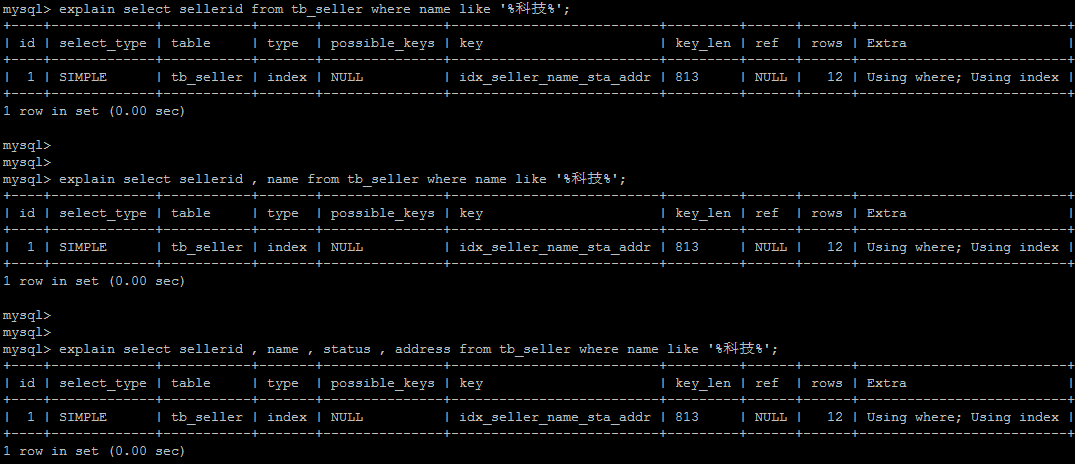
解决方案 :
通过覆盖索引来解决 (不用 select *)
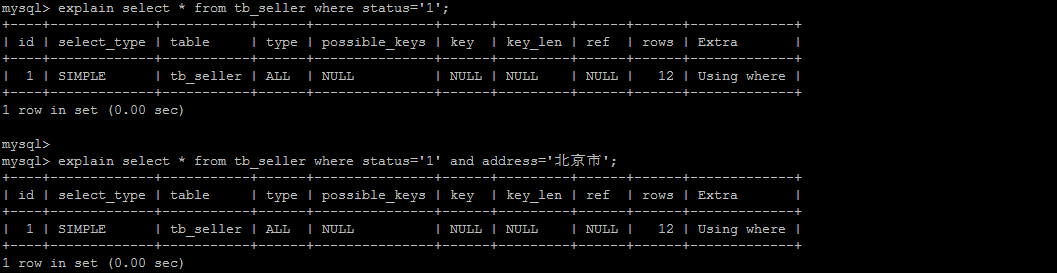
# 9).如果MySQL评估使用索引比全表更慢,则不使用索引。
我们先给 address 创建索引
create index idx_seller_address on tb_seller(address);
在我们表 tb_seller 中,12条地区数据其中11个是北京市
查北京地区的走全表扫描
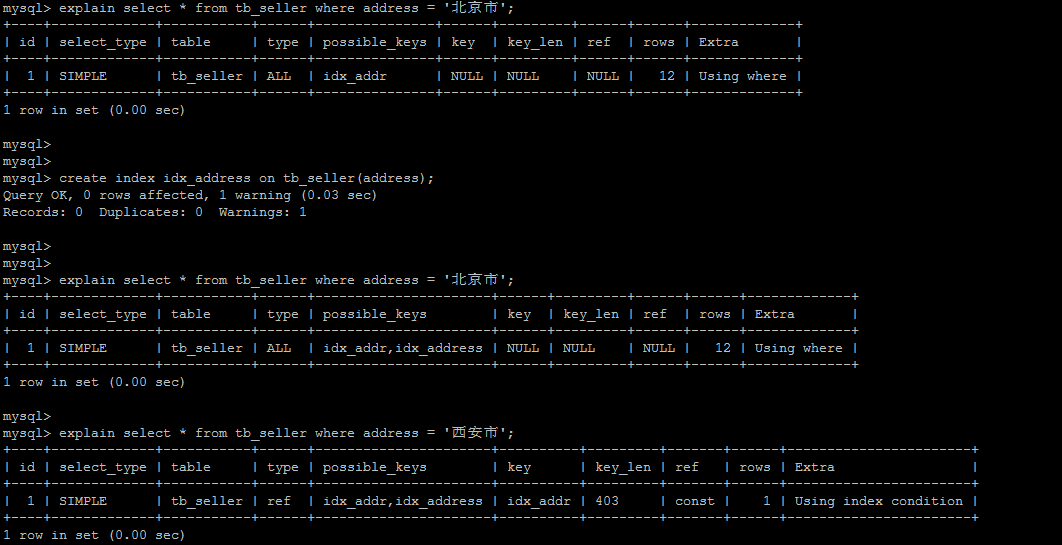
使用覆盖查询会走索引
explain select address from tb_seller where address='北京市';
# 10).is NULL,is NOT NULL 有时索引失效。
和上一条(9)差不多,
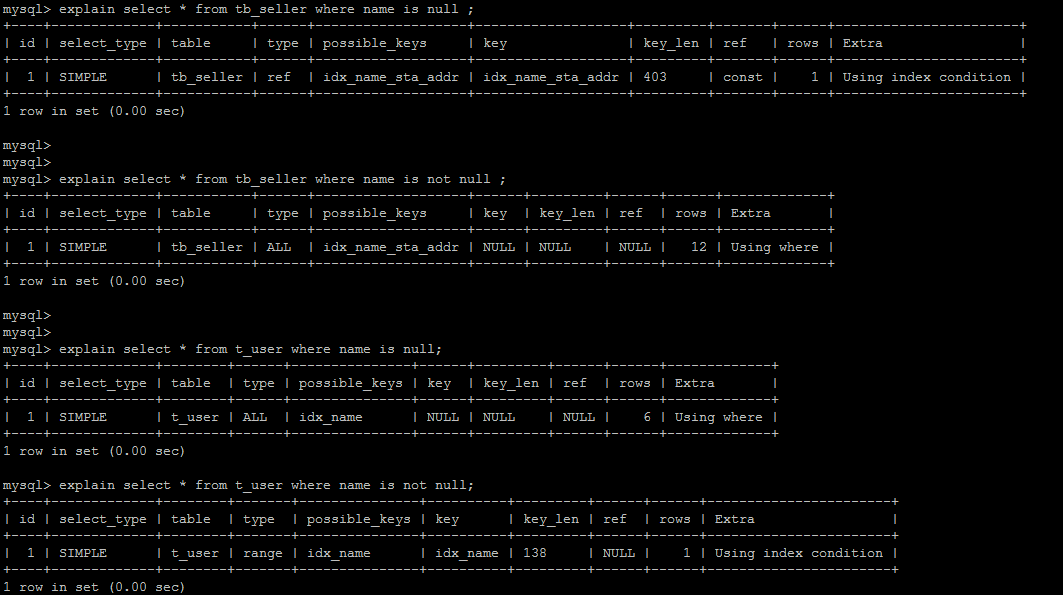
# 11).in走索引,not in 索引失效。
在mysql 5.6中
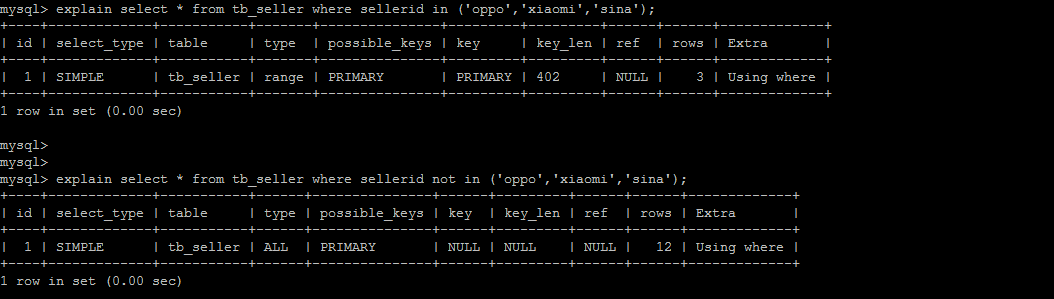
个人理解:not in 判断不存在的,需要对表进行大部分数据扫描,类似于第九条
mysql 5.7中都不失效:
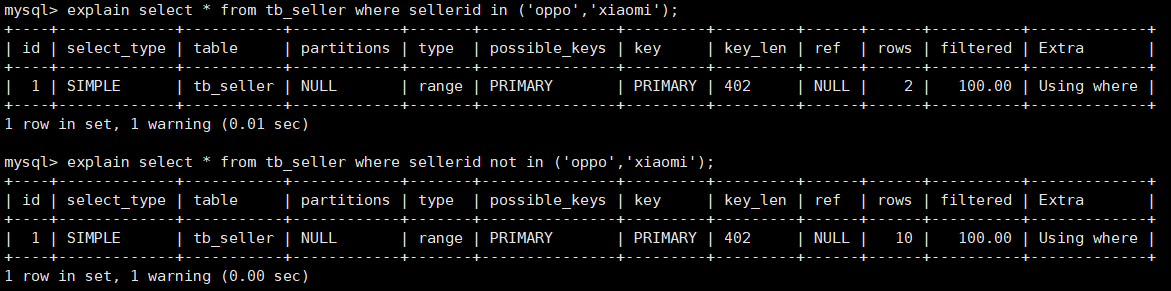
# 12).单列索引和复合索引。
尽量使用复合索引,而少使用单列索引 。
创建复合索引
create index idx_name_sta_address on tb_seller(name, status, address);
--就相当于创建了三个索引 :
-- name
-- name + status
-- name + status + address
2
3
4
5
6
创建单列索引
create index idx_seller_name on tb_seller(name);
create index idx_seller_status on tb_seller(status);
create index idx_seller_address on tb_seller(address);
2
3
数据库会选择一个最优的索引(辨识度最高索引)来使用,并不会使用全部索引 。
# 13).使用OR
如果 SQL 中使用了 OR 条件,OR 前的条件列有索引,而后面的列没有索引的话,那么涉及到的索引都不会使用
# 14).使用order by
1.下面的情况是会使用索引的
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx and c4=xx order by c3 #这种情况是会使用索引的,c1,c2都用上了,且c3实际也算用上了,因为它用来排序了(索引的作用就是查找和排序) select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx and order by c3 #这两句一样的效果1
2
3
42.这时,因为跳过c3对c4排序,c4就没有参与排序,这时是 Using filesort
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx order by c4 #Using filesort13.此种情况,并没有索引失效,虽然使用的const只有c1,但c2、c3也参与了排序(未失效原因是MySQL底层优化)
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c5=xx order by c2,c3 #const 114.order by中并没有受到MySQL的优化,其顺序依然是c3,c2,与索引字段相反了,而
使用到的索引只走了c1,没有跟着走c2,然后后面接着的是order by的c3,c2而不是c2c3,所以order by的c3,c2失效了,出现了Using filesortselect * from xxx where c1=xx and c5=xx order by c3,c2 #const1 Using filesort15.在 order by 操作中,排序的列同时也在 where 语句中,是会使用索引的。这里会用到c1,c2两个const,并且c2,c3参与排序
#这两句效果一样 select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx order by c2,c3 #const 1 2 select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx and c5=xxx order by c2,c3 #const 1 21
2
36.此时会用到c1,c2两个const,因为走了c1,c2,后面order by又是c3开始的,所以c3参与排序,而且由于c2在where中已经查找出来了,在排序的时候已经是一个常量,就不会参与排序,不会产生Using filesort
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c2=xx and c5=xxx order by c3,c2 #const 1 217.下面这条使用了group by,因为group by分组之前必定会先排序,所以走了c1一个const,没有产生filesort
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c4=xx group by c2,c3 #const 11而下面的就不一样,不仅产生Using filesort,还产生了Using temporary。
同样是因为group by分组之前必定会先排序,而排序的索引顺序乱了,会导致临时表产生
select * from xxx where c1=xx and c4=xx group by c3,c2 #const 1 Using filesort Using temporary1
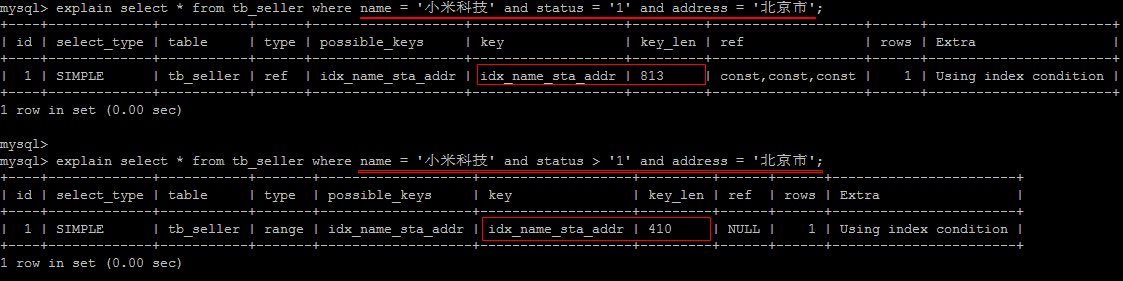
# 15).使用<>,!=
在索引字段上使用 <>,!=。不等于操作符是永远不会用到索引的,因此对它的处理只会产生全表扫描。
但是如果在复合索引中,只会失效使用<> !=符号之后的索引字段,之前的会生效,且该使用<> !=的索引字段会生效一部分,用于排序
上面的结果最终取决于MySQL底层优化后的,即第几个索引字段使用了<> !=,它后面的会失效,它前面的不会失效
# 查看索引使用情况
在 MySQL 索引的使用过程中,有一个
Handler_read_key值,这个值表示了某一行被索引值读的次数。 Handler_read_key 的值比较低的话,则表明增加索引得到的性能改善不是很理想,可能索引使用的频率不高。还有一个值是
Handler_read_rnd_next,这个值高则意味着查询运行效率不高,应该建立索引来进行抢救。这个值的含义是在数据文件中读下一行的请求数。如果正在进行大量的表扫描,Handler_read_rnd_next 的值比较高,就说明表索引不正确或写入的查询没有利用索引。
show status like 'Handler_read%'; --当前会话级别
show global status like 'Handler_read%'; --全局级别
2
3

Handler_read_first
索引中第一条被读的次数。如果较高,表示服务器正执行大量全索引扫描(这个值越低越好)。
Handler_read_key
如果索引正在工作,这个值代表一个行被索引值读的次数,如果值越低,表示索引得到的性能改善不高,因为索引不经常使用(这个值越高越好)。
Handler_read_next
按照键顺序读下一行的请求数。如果你用范围约束或如果执行索引扫描来查询索引列,该值增加。
Handler_read_prev
按照键顺序读前一行的请求数。该读方法主要用于优化ORDER BY ... DESC。
Handler_read_rnd
根据固定位置读一行的请求数。如果你正执行大量查询并需要对结果进行排序该值较高。你可能使用了大量需要MySQL扫描整个表的查询或你的连接没有正确使用键。这个值较高,意味着运行效率低,应该建立索引来补救。
Handler_read_rnd_next
在数据文件中读下一行的请求数。如果你正进行大量的表扫描,该值较高。通常说明你的表索引不正确或写入的查询没有利用索引。
# 练习
假设 index(a,b,c);
| Where 语句 | 索引是否被使用 |
|---|---|
| where a = 3 | Y,使用到 a |
| where a = 3 and b = 5 | Y,使用到 a,b |
| where a = 3 and b = 5 and c = 4 | Y,使用到 a,b,c |
| where b = 3 或者 where b = 3 and c = 4 或者 where c = 4 | N(第二条,左前缀法则) |
| where a = 3 and c = 5 | 使用到 a, 但是 c 不可以,b 中间断了 |
| where a = 3 and b > 4 and c = 5 | 使用到 a 和 b, c 不能用在范围之后,b 断了 |
| where a is null and b is not null | is null 支持索引 但是 is not null 不支持 |
| where a <> 3 | 不能使用索引 |
| where abs(a) =3 | 不能使用索引 |
| where a = 3 and b like 'kk%' and c = 4 | Y,使用到 a,b,c |
| where a = 3 and b like '%kk' and c = 4 | Y,只用到 a |
| where a = 3 and b like '%kk%' and c = 4 | Y,只用到 a |
| where a = 3 and b like 'k%kk%' and c = 4 | Y,使用到 a,b,c |