框架
框架
Table of Contents generated with DocToc (opens new window)
# 思维导图
# Spring IOC
参考文章:Spring IOC源码分析 (opens new window)
# Spring AOP的实现原理
参考文章:Spring AOP使用介绍 (opens new window)
参考文章:Spring AOP源码解析 (opens new window)
# SpringMVC各组件功能总结:
组件
# MultipartResolver
MultipartResolver用于处理上传请求,通过将普通的请求包装成MultipartHttpServletRequest来实现。MultipartHttpServletRequest可以通过getFile()方法直接获得文件。如果上传多个文件,还可以调用getFileMap()方法得到 Map< FileName, File> 这样的结构。
总结:MultipartResolver的作用就是封装普通的请求,使其拥有文件上传的功能# LocaleResolver
ViewResolver组件的resolveViewName()方法需要两个参数,一个是视图名,另一个就是Locale。参数Locale是从哪来的呢?这就是LocaleResolver组件要做的事。LocaleResolver用于从请求中解析出 Locale,比如在中国Locale当然就是zh-CN,用来表示一个区域。这个组件也是i18n的基础。
# ThemeResolver
从名字便可看出,ThemeResolver组件是用来解析主题的。
主题就是样式、图片及它们所形成的显示效果的集合。Spring MVC中一套主题对应一个properties文件,里面存放着与当前主题相关的所有资源,如图片、CSS样式等。创建主题非常简单,只需准备好资源,然后新建一个“主题名.properties”并将资源设置进去,放在classpath下,之后便可以在页面中使用了。SpringMVC中与主题有关的类有ThemeResolver、ThemeSource和Theme。ThemeResolver负责从请求中解析出主题名,ThemeSource则根据主题名找到具体的主题,其抽象也就是Theme,可以通过Theme来获取主题和具体的资源# HandlerMapping(重点)
HandlerMapping是用来查找Handler的,也就是处理器,具体的表现形式可以是类,也可以是方法。比如,标注了@RequestMapping的每个方法都可以看成一个Handler。Handler负责实际的请求处理,在请求到达后,HandlerMapping的作用便是找到请求相应的处理器Handler和Interceptor,
拦截器的pre方法会在Handler执行前执行,post方法会在Handler执行并拿到ModelAndView后执行# HandlerAdapter(重点)
从名字上看,HandlerAdapter是一个适配器。因为SpringMVC中Handler可以是任意形式的,只要能够处理请求便可。但是把请求交给Servlet的时候,由于Servlet的方法结构都是doService(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp)形式的,要让固定的Servlet处理方法调用Handler来进行处理,这一步工作便是HandlerAdapter要做的事,
实质的handler执行也就是交给HandlerAdapter做的# HandlerExceptionResolver
从组件的名字上看,HandlerExceptionResolver是用来处理Handler产生的异常情况的组件。具体来说,此组件的作用是根据异常设置ModelAndView,之后交给渲染方法进行渲染,渲染方法会将ModelAndView渲染成页面。不过要注意,HandlerExceptionResolver只用于解析对请求做处理阶段产生的异常,渲染阶段的异常不归它管,这也是Spring MVC 组件设计的一大原则—分工明确、互不干涉
# RequestToViewNameTranslator
RequestToViewNameTranslator组件的作用是从请求中获取ViewName。因为ViewResolver根据ViewName查找View,但有的Handler处理完成之后,没有设置View,也没有设置ViewName,便要通过这个组件来从请求中查找ViewName
# ViewResolver
ViewResolver即视图解析器。通常在Spring MVC的配置文件中,都会配上一个实现类来进行视图解析。这个组件的主要作用是将String类型的视图名和Locale解析为View类型的视图,只有一个resolveViewName()方法。从方法的定义可以看出,Controller层返回的String类型的视图名viewName最终会在这里被解析成为View。View是用来渲染页面的,也就是说,它会将程序返回的参数和数据填入模板中,生成HTML文件。ViewResolver在这个过程中主要做两件大事:ViewResolver会找到渲染所用的模板(第一件大事)和所用的技术(第二件大事,其实也就是找到视图的类型,如JSP)并填入参数。默认情况下,SpringMVC会为我们自动配置一个InternalResourceViewResolver,是针对JSP类型视图的
# FlashMapManager
说到FlashMapManager组件,得先说一下FlashMap。 FlashMap用于重定向时的参数传递,比如在处理用户订单时,为了避免重复提交,可以处理完post请求后重定向到一个get请求,这个get请求可以用来显示订单详情之类的信息。这样做虽然可以规避用户重新提交订单的问题,但是在这个页面上要显示订单的信息,这些数据从哪里获取呢?因为重定向是没有传递参数这一功能的,如果不想把参数写进URL(其实也不推荐这么做,除了URL有长度限制,把参数都直接暴露也不安全),那么就可以通过FlashMap来传递。只需要在重定向之前将要传递的数据写入请求(可以通过ServletRequestAttributes.getRequest()方法获得)的属性OUTPUT_FLASH_MAP_ATTRIBUTE中,这样在重定向之后的Handler中Spring就会自动将其设置到Model中,在显示订单信息的页面上就可以直接从Model中获得数据。 FlashMapManager就是用来管理FlashMap的。
# SpringMVC的初始化流程
# SpringMVC的执行流程(不涉及初始化)
# 在doService方法里面初始化这个请求的一些属性
包括但不限于:Spring管理的的Web容器上下文、国际化解析器、主题解析器
# 执行doService方法中的doDispatch方法
# 1.先检查这个请求是不是文件上传multipart请求
如果是则先进行一些处理
# 2.获取HandlerExecutionChain处理执行链
mappedHandler = getHandler(processedRequest);1
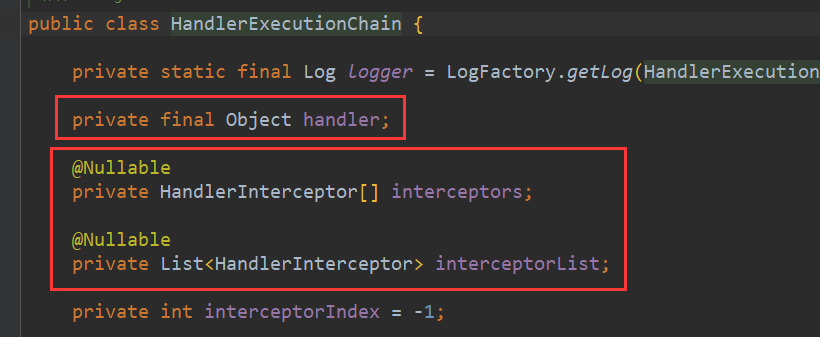
HandlerExecutionChain对象就有处理请求的handler对象,即处理请求的Controller中的方法,还有能对这个handler进行处理的拦截器列表
通过
getHandlerInternal方法拿到HandlerMethod获取流程
通过拿到请求的路径(RequestMapping中的),把这个路径set到request的属性里面,然后获取到读写锁中的读锁,再去获取HandlerMethod
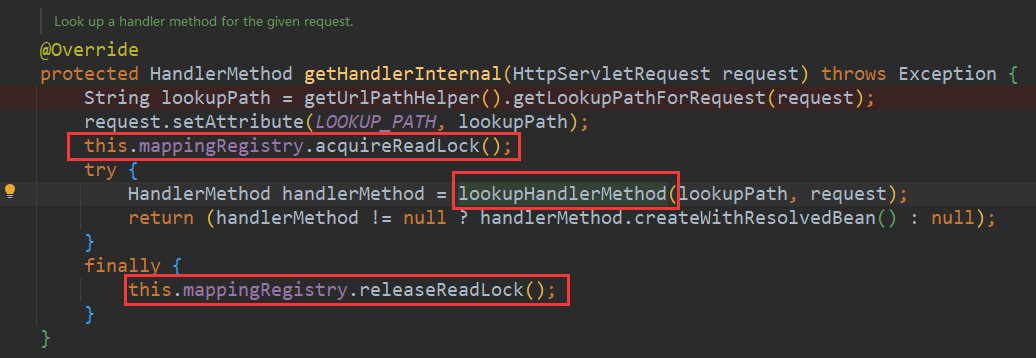
进入
lookupHandlerMethod方法,先在mappingRegistry里面根据url获取到请求(格式为:{GET /test})。如果有多个匹配还需要进行排序,不赘述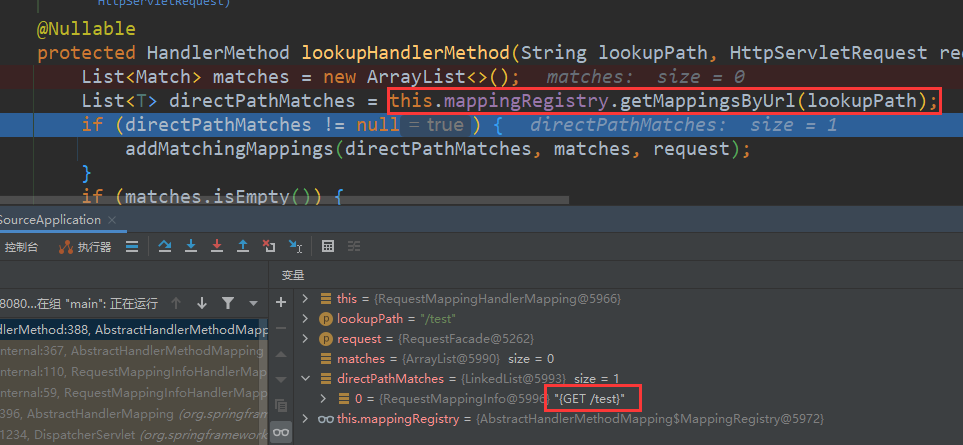
根据这个请求去获取处理的方法:
this.mappingRegistry.getMappings().get(mapping)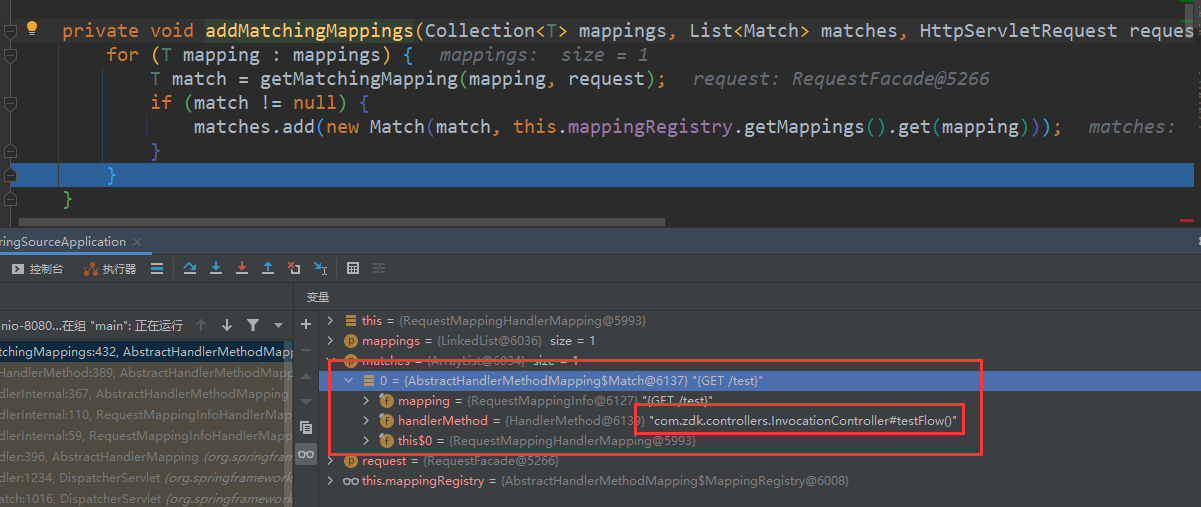
做完以上步骤之后就是往request属性中set一些属性
拿到后去获取HandlerExecutionChain
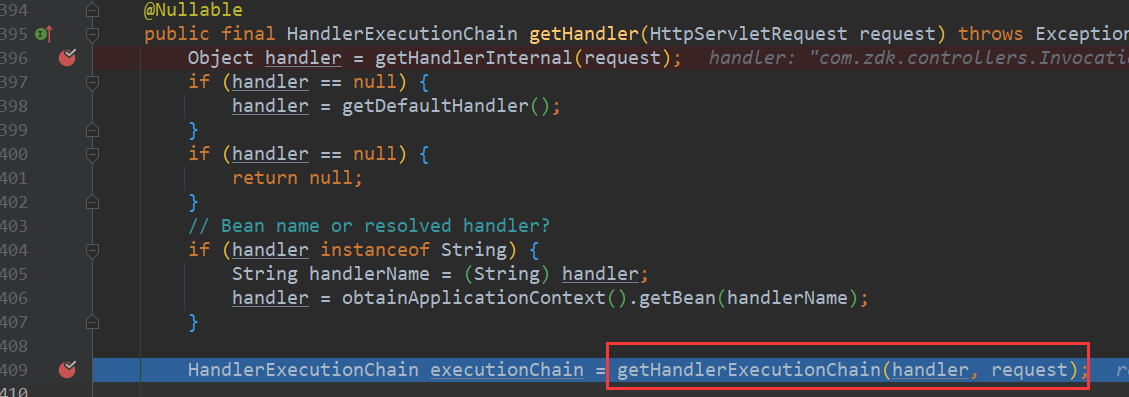
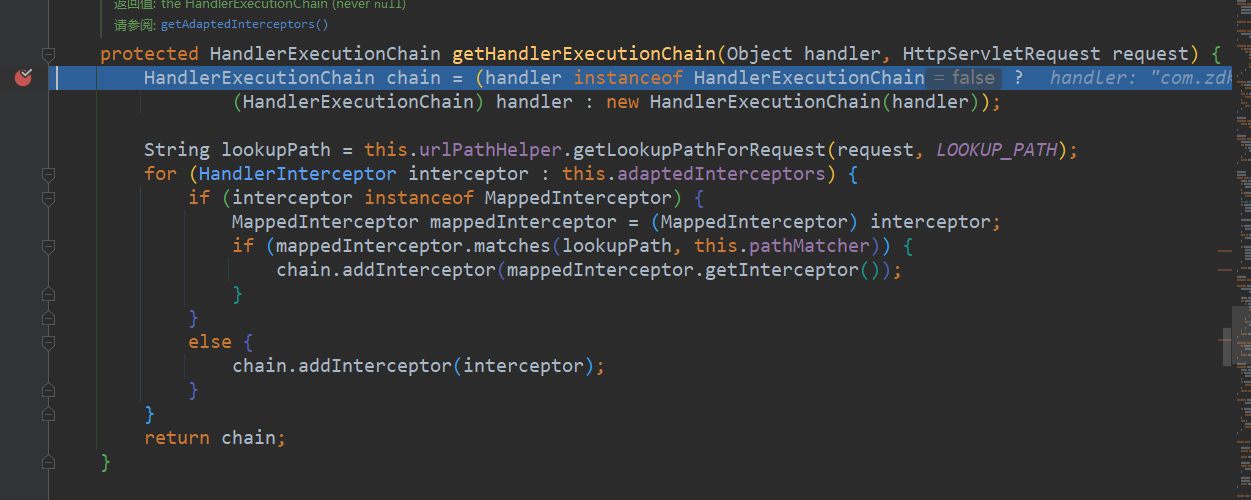
这里实际是获取能够拦截当前请求的所有拦截器,然后将其封装到一个已有或新new的HandlerExecutionChain里面,获取到后,进行跨域的处理,然后返回这个处理执行链
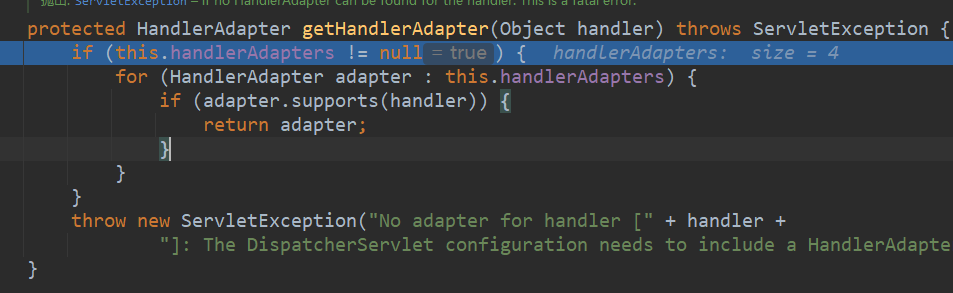
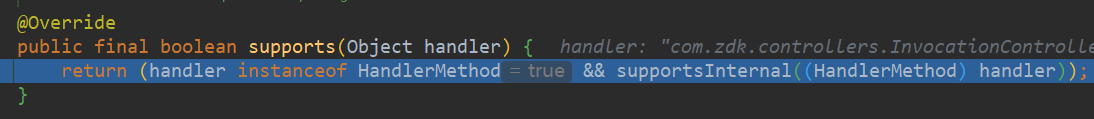
# 3.上一步拿到了handler和对应的拦截器了,这一步是获取当前请求的处理器适配器
寻找adapters中一个support当前handler的adapter,support条件是:这个handler是HandlerMethod及其子类
# 4.通过获取到的处理器适配器进行真正的请求处理
// Actually invoke the handler.
//返回一个ModelAndView
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
2
3
第一步先检查当前的处理器适配器是否支持当前请求的request method
protected final void checkRequest(HttpServletRequest request) throws ServletException { // Check whether we should support the request method. String method = request.getMethod(); if (this.supportedMethods != null && !this.supportedMethods.contains(method)) { throw new HttpRequestMethodNotSupportedException(method, this.supportedMethods); } // Check whether a session is required. if (this.requireSession && request.getSession(false) == null) { throw new HttpSessionRequiredException("Pre-existing session required but none found"); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12然后看是否需要使用synchronize同步处理请求,最后均调用
invokeHandlerMethod方法进行处理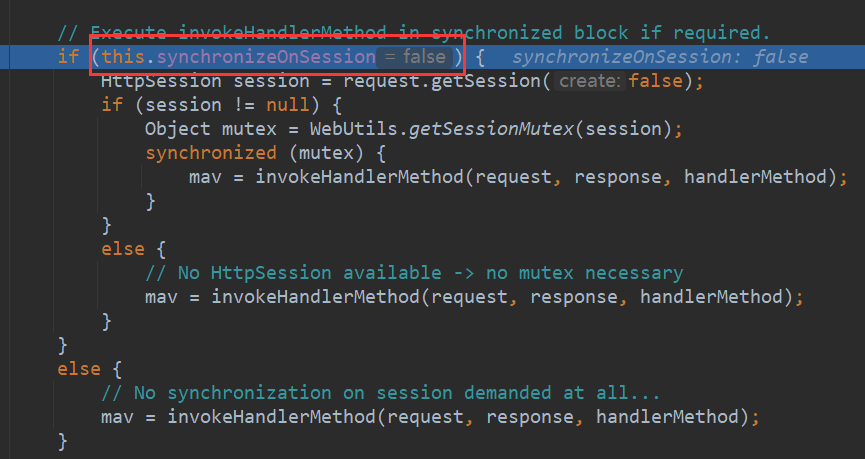
进入到invokeHandlerMethod方法
@Nullable protected ModelAndView invokeHandlerMethod(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HandlerMethod handlerMethod) throws Exception { ServletWebRequest webRequest = new ServletWebRequest(request, response); try { //首先获取一个 WebDataBinderFactory 对象,该对象将用来构建 WebDataBinder WebDataBinderFactory binderFactory = getDataBinderFactory(handlerMethod); //接下来获取一个 ModelFactory 对象,该对象用来初始化/更新 Model 对象 ModelFactory modelFactory = getModelFactory(handlerMethod, binderFactory); //接下来创建 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod 对象,一会方法的调用,将由它完成 ServletInvocableHandlerMethod invocableMethod = createInvocableHandlerMethod(handlerMethod); //接下来给 invocableMethod 把需要的参数都设置好 if (this.argumentResolvers != null) { //参数的处理器 invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodArgumentResolvers(this.argumentResolvers); } if (this.returnValueHandlers != null) { //返回值的处理器 invocableMethod.setHandlerMethodReturnValueHandlers(this.returnValueHandlers); } invocableMethod.setDataBinderFactory(binderFactory); invocableMethod.setParameterNameDiscoverer(this.parameterNameDiscoverer); //构造一个 ModelAndViewContainer 对象,将来用来存储 Model 和 View ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer = new ModelAndViewContainer(); //把 FlashMap 中的数据先添加进 ModelAndViewContainer 容器中 mavContainer.addAllAttributes(RequestContextUtils.getInputFlashMap(request)); //接下来初始化 Model,处理 @SessionAttributes 注解和 WebDataBinder 定义的全局数据,同时配置是否在重定向时忽略 defaultModel modelFactory.initModel(webRequest, mavContainer, invocableMethod); mavContainer.setIgnoreDefaultModelOnRedirect(this.ignoreDefaultModelOnRedirect); //接下来处理异步请求情况,判断是否有异步请求结果 AsyncWebRequest asyncWebRequest = WebAsyncUtils.createAsyncWebRequest(request, response); asyncWebRequest.setTimeout(this.asyncRequestTimeout); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.setTaskExecutor(this.taskExecutor); asyncManager.setAsyncWebRequest(asyncWebRequest); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptors(this.callableInterceptors); asyncManager.registerDeferredResultInterceptors(this.deferredResultInterceptors); if (asyncManager.hasConcurrentResult()) { Object result = asyncManager.getConcurrentResult(); mavContainer = (ModelAndViewContainer) asyncManager.getConcurrentResultContext()[0]; asyncManager.clearConcurrentResult(); LogFormatUtils.traceDebug(logger, traceOn -> { String formatted = LogFormatUtils.formatValue(result, !traceOn); return "Resume with async result [" + formatted + "]"; }); invocableMethod = invocableMethod.wrapConcurrentResult(result); } //调用 invokeAndHandle 方法去真正执行接口方法 invocableMethod.invokeAndHandle(webRequest, mavContainer); //如果是异步请求,则直接返回即可 if (asyncManager.isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { return null; } //接下来调用 getModelAndView 方法去构造 ModelAndView 并返回,在该方法中,首先会去更新 Model,更新的时候会去处理 SessionAttribute 同时配置 BindingResult;然后会根据 ModelAndViewContainer 去创建一个 ModelAndView 对象;最后,如果 ModelAndViewContainer 中的 Model 是 RedirectAttributes 类型,则将其设置到 FlashMap 中 return getModelAndView(mavContainer, modelFactory, webRequest); } finally { //最后设置请求完成 webRequest.requestCompleted(); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61调用 invokeAndHandle 方法去真正执行接口方法
public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs); setResponseStatus(webRequest); //....下面的省略 }1
2
3
4
5
6
7最终是通过反射去执行的:
从
invokeForRequest->doInvoke(args)->getBridgedMethod().invoke(getBean(), args)getBridgedMethod()方法获取的就是Controller中处理当前请求的方法,即handler
public Object invoke(Object obj, Object... args) throws IllegalAccessException, IllegalArgumentException, InvocationTargetException { if (!override) { if (!Reflection.quickCheckMemberAccess(clazz, modifiers)) { Class<?> caller = Reflection.getCallerClass(); checkAccess(caller, clazz, obj, modifiers); } } MethodAccessor ma = methodAccessor; // read volatile if (ma == null) { ma = acquireMethodAccessor(); } return ma.invoke(obj, args); }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16执行完后
拿到方法返回值,如果返回值为null,不用进行下面的处理;如果不为null,则要通过
returnValueHandlers返回值处理器对返回值进行处理,比如转JSON这种public void invokeAndHandle(ServletWebRequest webRequest, ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, Object... providedArgs) throws Exception { if (returnValue == null) { //... } else if (StringUtils.hasText(getResponseStatusReason())) { mavContainer.setRequestHandled(true); return; } mavContainer.setRequestHandled(false); Assert.state(this.returnValueHandlers != null, "No return value handlers"); try { //对返回值进行处理 this.returnValueHandlers.handleReturnValue( returnValue, getReturnValueType(returnValue), mavContainer, webRequest); } //... }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18最后获取ModelAndView并返回,然后设置请求已完成
private ModelAndView getModelAndView(ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer, ModelFactory modelFactory, NativeWebRequest webRequest) throws Exception {}1
2现在回到
handleInternal方法里面,方法执行完后,对缓存进行处理,最后返回ModelAndViewif (!response.containsHeader(HEADER_CACHE_CONTROL)) { if (getSessionAttributesHandler(handlerMethod).hasSessionAttributes()) { applyCacheSeconds(response, this.cacheSecondsForSessionAttributeHandlers); } else { prepareResponse(response); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8执行到这里回到了开始
doDispatch方法中了,然后来到这里mappedHandler.applyPostHandle(processedRequest, response, mv); void applyPostHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable ModelAndView mv) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { for (int i = interceptors.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; interceptor.postHandle(request, response, this.handler, mv); } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12这里是拿到ModelAndView以后,调用所有拦截器的postHandle方法进行后置处理
然后处理产生异常的情况,将ModelAndView赋值为异常时的mv,没有异常则不变
processDispatchResult(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler, mv, dispatchException); private void processDispatchResult(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable HandlerExecutionChain mappedHandler, @Nullable ModelAndView mv, @Nullable Exception exception) throws Exception { boolean errorView = false; if (exception != null) { if (exception instanceof ModelAndViewDefiningException) { logger.debug("ModelAndViewDefiningException encountered", exception); mv = ((ModelAndViewDefiningException) exception).getModelAndView(); } else { Object handler = (mappedHandler != null ? mappedHandler.getHandler() : null); //处理异常 比如将异常set到request的属性里面 mv = processHandlerException(request, response, handler, exception); errorView = (mv != null); } } // Did the handler return a view to render? if (mv != null && !mv.wasCleared()) { //渲染视图 render(mv, request, response); if (errorView) { WebUtils.clearErrorRequestAttributes(request); } } else { if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) { logger.trace("No view rendering, null ModelAndView returned."); } } if (WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request).isConcurrentHandlingStarted()) { // Concurrent handling started during a forward return; } if (mappedHandler != null) { // Exception (if any) is already handled.. mappedHandler.triggerAfterCompletion(request, response, null); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44如果异常被处理了,就来到这里
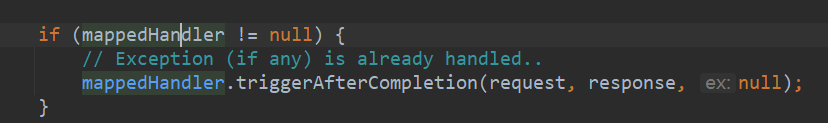
这个triggerAfterCompletion方法会依次调用所有已执行成功的拦截器的
afterCompletion方法来完成整个拦截器的调用流程void triggerAfterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, @Nullable Exception ex) throws Exception { HandlerInterceptor[] interceptors = getInterceptors(); if (!ObjectUtils.isEmpty(interceptors)) { for (int i = this.interceptorIndex; i >= 0; i--) { HandlerInterceptor interceptor = interceptors[i]; try { interceptor.afterCompletion(request, response, this.handler, ex); } catch (Throwable ex2) { logger.error("HandlerInterceptor.afterCompletion threw exception", ex2); } } } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15执行完后,进入到最后步骤,如果有文件上传,会清楚文件上传使用过的资源,至此,
doDispatch方法执行完毕,返回到最开始的doService方法中进行异步的处理以后,由
DispatcherServlet中的doService方法进入到FrameworkServlet的processRequest方法的finally中(因为processRequest其实是入口)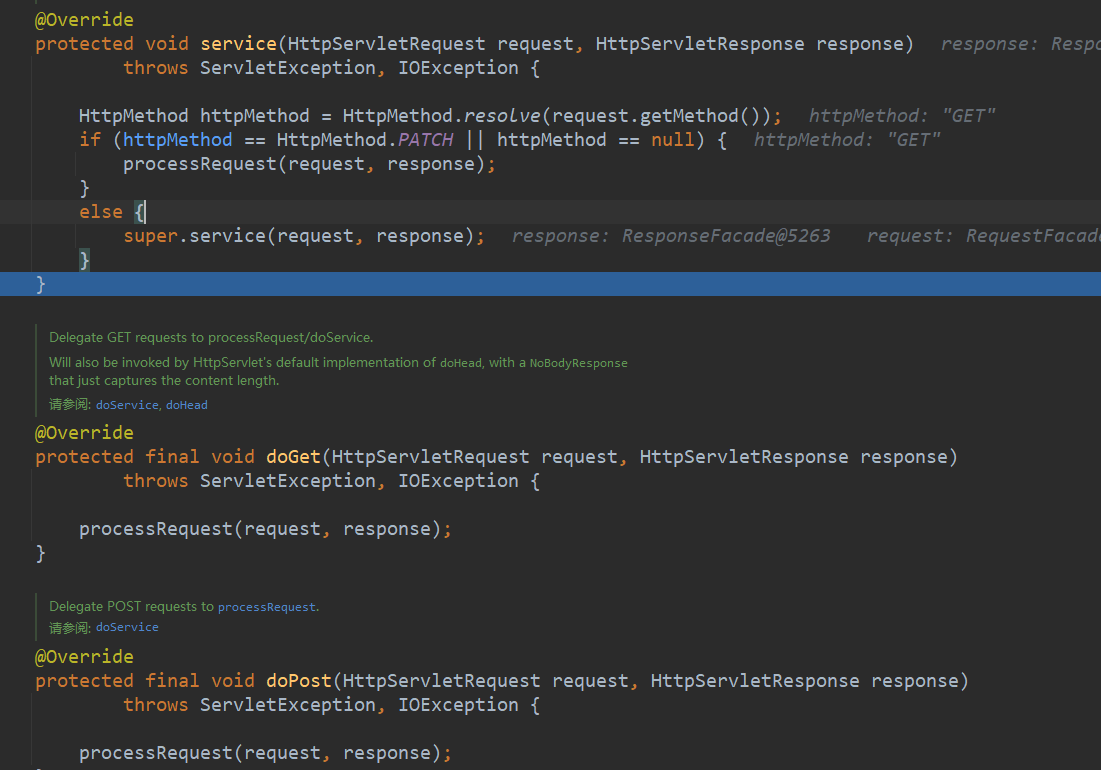
protected final void processRequest(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); Throwable failureCause = null; LocaleContext previousLocaleContext = LocaleContextHolder.getLocaleContext(); LocaleContext localeContext = buildLocaleContext(request); RequestAttributes previousAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes(); ServletRequestAttributes requestAttributes = buildRequestAttributes(request, response, previousAttributes); WebAsyncManager asyncManager = WebAsyncUtils.getAsyncManager(request); asyncManager.registerCallableInterceptor(FrameworkServlet.class.getName(), new RequestBindingInterceptor()); initContextHolders(request, localeContext, requestAttributes); try { doService(request, response); } catch (ServletException | IOException ex) { failureCause = ex; throw ex; } catch (Throwable ex) { failureCause = ex; throw new NestedServletException("Request processing failed", ex); } finally { resetContextHolders(request, previousLocaleContext, previousAttributes); if (requestAttributes != null) { requestAttributes.requestCompleted(); } logResult(request, response, failureCause, asyncManager); publishRequestHandledEvent(request, response, startTime, failureCause); } }1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38执行完后进入
ApplicationFilterChain中的internalDoFilter中的finally,实质是执行请求开始进来时的一系列过滤器的doFilter方法,所以知道请求刚进入时,先执行了过滤器最后响应结果,整个流程完毕